Tear gas has been used in a number of incidents in recent months in Iraq, France, Chile, Hong Kong, and elsewhere. Numerous allegations about tear gas have been made, and misinformation, half-truths, myth, and suppositions have been passed around on social media.
Yet there is actually a wealth of information about tear gas available in the technical literature. The purpose of this post is to dig into the health and safety concerns behind tear gas usage.
What Is “Tear Gas”?
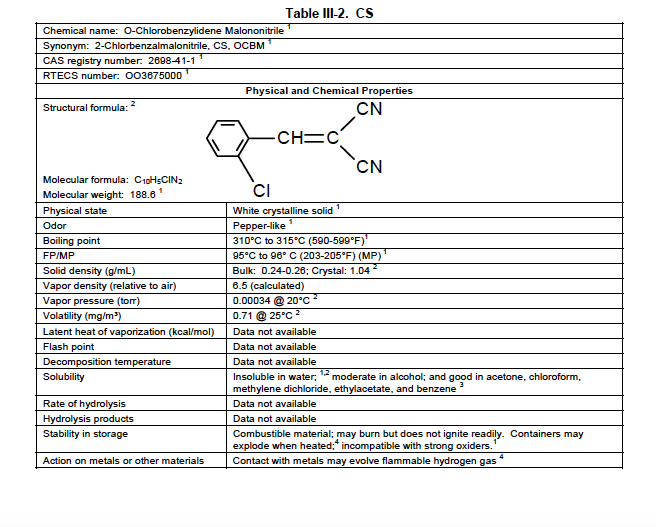
Generally, the term “tear gas” refers to a substance known as CS. CS, in turn, is a nickname for chemical substance 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile. It is not a gas in normal situations for very long. CS is generally a solid, and is used in many forms.
CS is often used in burning grenades or canisters where the CS is combined with a burning filler and the resulting smoke suspends a cloud of particulates. In such form, CS can be an area-weapon, with clouds of fog or smoke used to clear buildings or large areas. Others dissolve CS in a solvent for spraying or bursting to suspend a cloud of particulates. CS is extremely irritating to skin and eyes, and has a distinct peppery smell. It is commonly used in military training as a simulant for much more dangerous substances and to help soldiers learn to put on their protective masks quickly.
It should be noted that there are other riot control agents that have been used, either historically, or in modern times. CA, CN, CR, OC (aka “Pepper Spray”), and various other compounds have been used at various points. There have been situations, such as in Iraq, where hexachloroethane (HC) smoke grenades have been used, in an unacceptable off-label usage, with or instead of tear gas grenades. However, there is little evidence that anything other than CS is in use in the current situation in Hong Kong.
Terminology is important. Some social media references to CS or other riot control agents as “nerve agents” or “mustard gas” are factually incorrect. A widely circulated myth alleges that because CS and pepper spray cause pain, and pain is transmitted by the nerves, these are therefore “nerve agents.” This is not, in fact, anything close to the actual definition of nerve agents. This has been discussed at length in another Bellingcat article.
The physical characteristics of CS are shown in this table from the US Army’s Field Manual 3-11-9:
 Toxicity Of CS
Toxicity Of CS
CS has been widely considered a relatively safe substance to use because it has a very wide margin between the concentrations at which it is intolerable or incapacitating, and the concentrations at which it is potentially lethal.
Studies and references vary somewhat, but an accepted reference work (R. Gupta, Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents, 2nd edition, 2015, Elsevier) gives well-sourced data. CS provides irritation starting at a very low threshold of 0.004 milligrams per cubic meter of air (mg/m3).
This is an extremely small amount of material. Intolerable or incapacitating levels of CS are around 3-10 mg/m3, although individual tolerances vary significantly. Estimated lethal concentration of CS range from 25,000 to 150,000 mg/m3, over the course of one minute. This level of CS is basically impossible to achieve in any kind of field conditions.
There have been very few cases of direct lethality from CS exposure in humans, and a number of those have been due to fire and blunt trauma (from CS projectiles hitting the body), not actual CS exposure. A more comprehensive study of lethality from tear gas is here.
Vulnerable Populations
Some people are more vulnerable to CS exposure than others. CS particles are known to cause eye injury and people with contact lenses can have these particles get stuck behind the lenses, causing a higher degree of irritation than “normal.”
CS is a respiratory irritant and people with pre-existing lung conditions like asthma, emphysema, or recent smoke inhalation are likely to be more vulnerable to CS exposure. The literature on CS and asthma is inconclusive. One study has shown that women are more seriously affected by the respiratory effects of CS than men. Effects on children, pregnant women, and elderly people are poorly studied as there is no way to construct a research project on this in a way that conforms to ethical standards and there is also not enough case history from which to draw conclusions.
Four Categories Of CS Dispersal
If one examines the technical literature, not all CS is created equal, nor does every type of munition create CS with the same characteristics. The quality of CS produced by a munition appears to change depending on the method of dispersal.
Category 1: Sprays Of CS Liquid
First, there are devices that spray CS dissolved in solvents. These spray devices are commonly used by police. They are also legal for personal self-defence in many parts of the world. In the U.S., these are largely considered older technology and have been supplanted by pepper spray, which comes from chili peppers. In this category of device, the CS is dissolved in a solvent such as methylene chloride.
Category 2: Mechanical Or Explosive Dispersion Of Powder
Some devices are designed to disperse CS in powder form. One common form is the bursting grenade, of which the US M25A2 grenade is a classic example. It uses a small bursting charge to break open the grenade case and create a cloud of CS particles. Various fogger-type devices have been historically used, particularly in the Vietnam war, to make clouds of particles.
Category 3: Heat-Based Non-Munition Devices
In U.S. military training, CS grenades aren’t often used in mask confidence training. Normal practice is to heat capsules of CS powder. One study of U.S. Army CS-generation methods cited a range of 150-300° C, with an average burning temperature of 257° C. This particular study references devices used to heat and melt CS capsules in U.S. military training chambers. However, as these are used in military training in confined spaces, but not for riot control or law enforcement uses, they are not worthy of further discussion here.
Category 4: Burning CS Munitions
The largest category of CS devices are munitions that disperse the CS using a burning filler to create a smoke cloud. CS melts at 93-96° C and boils at 310-315° C.
The burning fillers, which are discussed at length below, heat up the CS, which vaporises and almost immediately condenses again, forming a smoke cloud. There is some possibility that solid CS particles also get suspended in the smoke from the burning fillers. It is this category of CS munition that poses the most hazards to health and property, for reasons that will be explained below.
Temperature Of Burning CS Munitions
Burning CS munitions will burn at various temperatures. Again, this is not an area which has received a lot of systematic study, and there’s not much reference material explaining what temperatures various CS devices reach while burning. Indeed, anecdotally, even with the same type of grenade, there will be a range of burning temperatures, as precise temperature is not one of the design specifications for such devices.
Technical literature on the burning temperature of the U.S. or other western CS grenades is sparse. The 1966 Edgewood Study helpfully asserts that U.S. grenades burn at 300 to 800° C, which is truly a wide range of results. The scientists who wrote the study replicated the contents of various CS grenades and did a significant number of test burns, with temperatures in the 500s and 600s as common results. The highest was 793° C and the lowest was 493° C. Not every test burn had temperatures measured, as the authors were looking for other things, like the percentage of CS that was effectively disseminated.
Grenades from other sources can vary significantly in burning temperature. It is anecdotally reported that the Hong Kong police have been using a new type of CS grenade that burns much hotter than previously used munitions. These new grenades are alleged to have ingredients such as magnesium and aluminium powder. A limited study using thermal imaging attempted to measure the burning temperature of some of these CS devices and the highest temperature measured was 552.6° C. However, this is well within the range of U.S. devices studied in the 1966 study.
What Is Actually In A Burning Tear Gas Shell Or Projectile?
Only a portion of the contents of a given tear gas shell will be CS. For example, a U.S. military-specification M7A3 CS grenade has about 128g of CS in pellets and about 212g of filler. A wide variety of materials appear to have been used as the burning fillers over the previous decades. These have included such materials as sugar, sulphur, magnesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, Fuller’s earth, kaolin, potassium chlorate, and various other components. The contents of the U.S. Army CS burning munitions are discussed the 1966 study cited above.
It should be noted that the various roles of the chemicals in the filler are usually well established. Potassium perchlorate is an oxidizer. Sugars such as sucrose or lactose work as fuels. Magnesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, and Fuller’s earth work as moderators, slowing the rate of combustion. It is not at all clear that every CS munition has such moderating ingredients.
CS And Human Skin
Burning CS munitions can cause burns on human skin. The majority of the cases described in medical literature are from actual direct contact with burning grenades or projectiles. This is understandable, given the temperatures discussed above.
CS particles will be hot enough to cause thermal burns for some period of time, particularly close to the actual point of discharge. Both the smoke from burning fillers and the temporarily vaporised CS emitted from a burning grenade will be hot enough to cause burns. For example, persons using oven mitts or other improvised techniques to pick up burning CS grenades can easily be exposed to CS particles and vapours hot enough to burn skin.
Accidental And Deliberate Fires
It is very important to note that even burning grenades at the low end of the range of possible temperatures, a burning CS grenade or projectile can set other things on fire. Even spent grenades may still be hot enough under some circumstances to cause fires.
CS grenades have been known to malfunction and have a condition colloquially known as a “hang-fire” wherein the ignition fuze malfunctions in some way and the grenade or projectile starts burning later than intended. Such a grenade, swept up and put into a rubbish bin or trash-pile, can cause a significant fire long after its intended use. These scenarios raise all sorts of problems, as a complex modern urban environment has many kinds of combustible materials. Plastics, synthetic textiles and upholsteries, woods that have been treated with finishes and varnishes, cleaning chemicals, and various other materials can create a bewildering array of toxic materials when combusted.
Thermal Decomposition Of CS
There is a serious problem with heating CS to the temperatures encountered in burning CS munitions. Some portion of the CS will degrade into other chemicals.
This is not something that is particularly well-known or heavily studied, but I was able to find some significant scientific literature about what happens when CS is heated to very high temperatures, such as those at the middle and high end of the burning CS grenades.
Some studies occurred in the 1960s. In the late 1990s, a U.S. Army scientist, one Timothy Kluchinsky, studied this phenomenon and wrote his 2001 PhD dissertation on the subject. He has published extensively on the topic (one example is here).
In 1960, a Porton Down study in the UK identified and measured some CS thermal degradation products. CO, CO2, Cl-, NH4, N2O, C2H2, and water were all measured in CS. A 1969 U.S. Army study burnt CS and found CO, CO2, H2O, HCl, HCN, NH3, N2O2 and C2H2 in the smoke plume.
Kluchinksy’s studies in 2000 and 2001 used gas chromatography and mass spectrometry and discovered the presence of numerous compounds in the smoke from burning-type CS canisters. These chemicals include 4-chlorobenzylidenemalononitrile (an isomer of CS), 2-chlorobenzaldehyde, 2-chlorobenzonitrile, quinoline, 2-chlorobenzylcyanide, 1,2-dicyanobenzene, 3-(2-chlorophenyl)propynenitrile, cis- and transisomers of 2-chlorocinnamonitrile, 2,2-dicyano-3-(2-chlorophenyl)oxirane, 2-chlorodihydrocinnamonitrile,benzylidenemalononitrile, cis- and trans- isomers of 2-cyanocinnamonitrile, 2-chlorobenzylmalononitrile, 3-quinoline carbonitrile, and 3-isoquinoline carbonitrile.
The health effects and toxicology of this long list of substances are not very well studied. Kluchinsky commented that many of these compounds were created by CS molecules giving up either chlorine or cyanide. He eventually did work to quantify the amount of HCl (hydrogen chloride) and HCN (hydrogen cyanide) emitted by CS under various conditions.
Decomposition Of Fillers
The subject of CS grenade fillers is not well-studied and product literature often does not specify the ingredients in CS grenade fillers, particularly products produced outside the U.S. and European Union. There is no comprehensive compendium of filling materials for CS grenades and the toxicology of burning fillers is an area that has received comparatively little study. It is possible that some fillers produce toxic materials when burnt.
It is also possible that poor manufacturing practices have accidentally incorporated unusual materials into fillers. This is not an area with a high degree of regulatory standards, and it would not surprise me to find that various trace amounts of rubbish, such as plastics and metals, even floor-sweepings, end up in low-budget CS munitions. The possible scope of harm from such scenarios is nearly impossible to estimate, as the numerous variables are unknown.
What About Cyanides?
It is clear from the literature that HCN — that is, hydrogen cyanide gas — is one of the thermal decomposition products that can be created when CS breaks down at high temperatures. However, it is difficult to construct a hypothetical scenario whereby enough hydrogen cyanide is lighter than air.
This means that, in open air, it will rise and not build up. Not only that, the HCN produced from thermal decomposition of CS will be warmer than ambient air and rise even faster than if the HCN were at the same temperature. Cases of toxic exposure to hydrogen cyanide generally occur in confined spaces. Furthermore, HCN is flammable, and many of the situations and scenarios involved include high temperatures and open flames, so it is possible that the HCN would combust.
The concentrations of HCN that will cause injury or death in humans are reported differently in different reference books. Although there have been many deaths from HCN inhalation, there have been very few where the exact concentration of HCN was known, so these figures vary greatly based on different interpretations of laboratory tests with animals. It is not possible to take measurements on inhaled HCN in rabbits or guinea pigs and then directly use those measurements as indicative of toxicity in humans, for a variety of reasons. Scientists have argued for decades over the correct way to convert numbers from animal models into human equivalents. As a result, for HCN (and actually for many other toxic inhalation hazards), the calculated human toxicity will vary a fair bit.
A standard reference book lists the following concentrations for HCN, but does not define the effects rigorously: